Cladribine (trade names Leustatin, Litak and Movectro) is a drug used to treat hairy cell leukemia (HCL, leukemic reticuloendotheliosis) and multiple sclerosis. Its chemical name is 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine (2CDA).
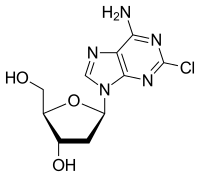
5-(6-Amino-2-chloro-purin-9-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol
As a purine analog, it is a synthetic anti-cancer agent that also suppresses the immune system. Chemically, it mimics the nucleosideadenosine and thus inhibits the enzyme adenosine deaminase, which interferes with the cell's ability to process DNA. It is easily destroyed by normal cells except for blood cells, with the result that it produces relatively few side effects and results in very little non-target cell loss.
Cladribine was designed by Dennis A. Carson as an anti-lymphocyte compound, while he was at The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California. It was first synthesized at Brigham Young University.The pharmacology and clinical applications were researched by scientists at Johnson and Johnson, which filed the New Drug Application and launched the drug in 1993.
Cladribine was designed based on information about an immune deficiency disease called adenosine deaminase deficiency. Carson described it as "a targeted agent directed against lymphocytes at a time when there was no such thing as targeted agents".
In 2008, Ernest Beutler of The Scripps Research Institute won the Wallace H. Coulter Award for Lifetime Achievement in Haematology from the Coulter Foundation and theAmerican Society of Hematology in part because of the clinical trials he ran, which established cladribine as the most effective treatment for hairy cell leukemia (HCL).
5-(6-Amino-2-chloro-purin-9-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol
As a purine analog, it is a synthetic anti-cancer agent that also suppresses the immune system. Chemically, it mimics the nucleosideadenosine and thus inhibits the enzyme adenosine deaminase, which interferes with the cell's ability to process DNA. It is easily destroyed by normal cells except for blood cells, with the result that it produces relatively few side effects and results in very little non-target cell loss.
Cladribine was designed by Dennis A. Carson as an anti-lymphocyte compound, while he was at The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California. It was first synthesized at Brigham Young University.The pharmacology and clinical applications were researched by scientists at Johnson and Johnson, which filed the New Drug Application and launched the drug in 1993.
Cladribine was designed based on information about an immune deficiency disease called adenosine deaminase deficiency. Carson described it as "a targeted agent directed against lymphocytes at a time when there was no such thing as targeted agents".
In 2008, Ernest Beutler of The Scripps Research Institute won the Wallace H. Coulter Award for Lifetime Achievement in Haematology from the Coulter Foundation and theAmerican Society of Hematology in part because of the clinical trials he ran, which established cladribine as the most effective treatment for hairy cell leukemia (HCL).

Fantastic - great job MD, and CC.
ReplyDelete